Improving Public Data for Building Segmentation from Convolutional Neural Networks for Fused Airborne Lidar and image data using active contours
ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2019
Abstract
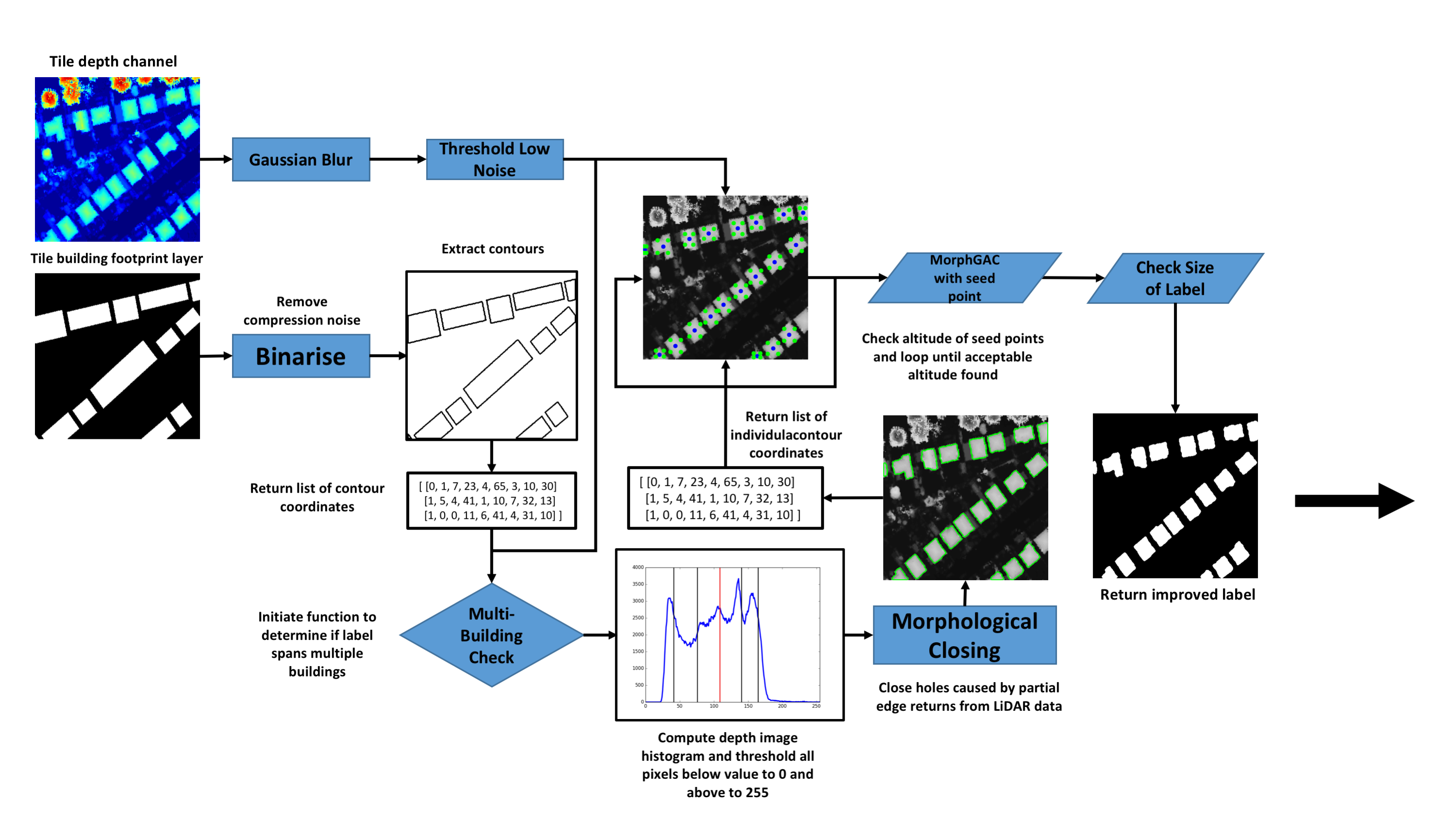
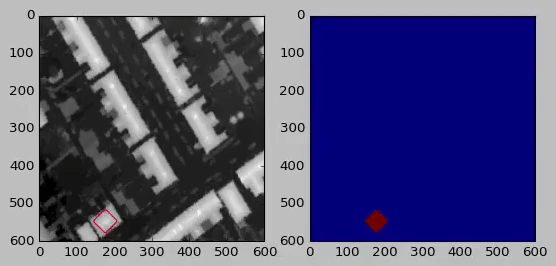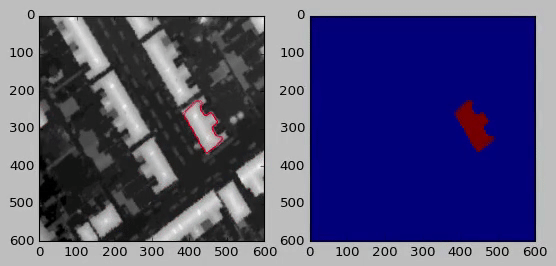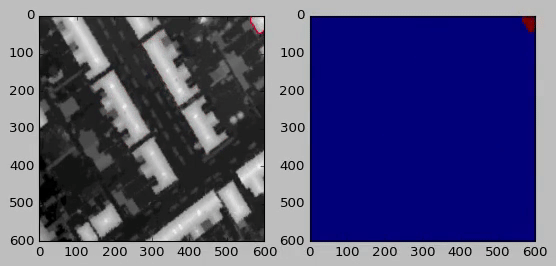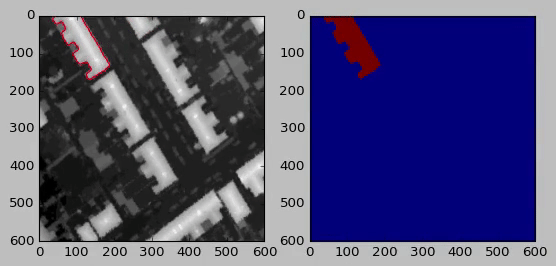
Robust and reliable automatic building detection and segmentation from aerial images/point clouds has been a prominent field of research in remote sensing, computer vision and point cloud processing for a number of decades. One of the largest issues associated with deep learning methods is the high quantity of data required for training. To help address this we present a method to improve public GIS building footprint labels by using Morphological Geodesic Active Contours (MorphGACs). We demonstrate by improving the quality of building footprint labels for detection and semantic segmentation, more robust and reliable models can be obtained. We evaluate these methods over a large UK-based dataset of 24556 images containing 169835 building instances. This is achieved by training several Mask/Faster R-CNN and RetinaNet deep convolutional neural networks. Networks are supplied with both RGB and fused RGB-lidar data. We offer quantitative analysis on the benefits of the inclusion of depth data for building segmentation. By employing both methods we achieve a detection accuracy of 0.92 (mAP@0.5) and segmentation f1 scores of 0.94 over a 4911 test images ranging from urban to rural scenes.
Cite
@article{griffiths2019improving,
title={Improving public data for building segmentation from Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) for fused airborne lidar and image data using active contours},
author={Griffiths, David and Boehm, Jan},
journal={ISPRS journal of photogrammetry and remote sensing},
volume={154},
pages={70--83},
year={2019},
publisher={Elsevier}
}
